Barium hydroxide

| |

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.470 |
| EC Number |
|
| 846955 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ba(OH)2 | |
| Molar mass | 171.34 g/mol (anhydrous) 189.355 g/mol (monohydrate) 315.46 g/mol (octahydrate) |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 3.743 g/cm3 (monohydrate) 2.18 g/cm3 (octahydrate, 16 °C) |
| Melting point | 78 °C (172 °F; 351 K) (octahydrate) 300 °C (monohydrate) 407 °C (anhydrous) |
| Boiling point | 780 °C (1,440 °F; 1,050 K) |
| mass of BaO (not Ba(OH)2): 1.67 g/100 mL (0 °C) 3.89 g/100 mL (20 °C) 4.68 g/100 mL (25 °C) 5.59 g/100 mL (30 °C) 8.22 g/100 mL (40 °C) 11.7 g/100 mL (50 °C) 20.94 g/100 mL (60 °C) 101.4 g/100 mL (100 °C)[citation needed] | |
| Solubility in other solvents | low |
| Basicity (pKb) | 0.15 (first OH–), 0.64 (second OH–)[1] |
| −53.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.50 (octahydrate) |
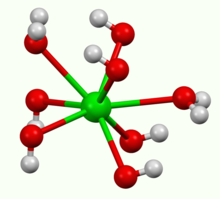
| Structure | |
| octahedral | |
| Thermochemistry[2] | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−944.7 kJ·mol−1 |
Enthalpy of fusion (ΔfH⦵fus)
|
16 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H314, H332, H412 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
308 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Fisher Scientific |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Barium oxide Barium peroxide |
Other cations
|
Calcium hydroxide Strontium hydroxide |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Barium hydroxide (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Barium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Ba(OH)2. The monohydrate (x = 1), known as baryta or baryta-water, is one of the principal compounds of barium. This white granular monohydrate is the usual commercial form.
Preparation and structure
[edit]Barium hydroxide can be prepared by dissolving barium oxide (BaO) in water:
- BaO + H2O → Ba(OH)2
It crystallises as the octahydrate, which converts to the monohydrate upon heating in air. At 100 °C in a vacuum, the monohydrate will yield BaO and water.[3] The monohydrate adopts a layered structure (see picture above). The Ba2+ centers adopt a square antiprismatic geometry. Each Ba2+ center is bound by two water ligands and six hydroxide ligands, which are respectively doubly and triply bridging to neighboring Ba2+ centre sites.[4] In the octahydrate, the individual Ba2+ centers are again eight coordinate but do not share ligands.[5]
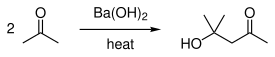
Uses
[edit]Industrially, barium hydroxide is used as the precursor to other barium compounds. The monohydrate is used to dehydrate and remove sulfate from various products.[6] This application exploits the very low solubility of barium sulfate. This industrial application is also applied to laboratory uses.
Laboratory uses
[edit]Barium hydroxide is used in analytical chemistry for the titration of weak acids, particularly organic acids. Its aqueous solution, if clear, is guaranteed to be free of carbonate, unlike those of sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, as barium carbonate is insoluble in water. This allows the use of indicators such as phenolphthalein or thymolphthalein (with alkaline colour changes) without the risk of titration errors due to the presence of carbonate ions, which are much less basic.[7]
Barium hydroxide is occasionally used in organic synthesis as a strong base, for example for the hydrolysis of esters[8] and nitriles,[9][10][11] and as a base in aldol condensations.
There are several uses for barium hydroxide such as to hydrolyse one of the two equivalent ester groups in dimethyl hendecanedioate.[12]
Barium hydroxide has also been used in the decarboxylation of amino acids liberating barium carbonate in the process.[13]
It is also used in the preparation of cyclopentanone,[14] diacetone alcohol[15] and D-gulonic γ-lactone.[16]
Reactions
[edit]Barium hydroxide decomposes to barium oxide when heated to 800 °C. Reaction with carbon dioxide gives barium carbonate. Its aqueous solution, being highly alkaline, undergoes neutralization reactions with acids. It is especially useful on reactions that require the titrations of weak organic acids. Thus, it forms barium sulfate and barium phosphate with sulfuric and phosphoric acids, respectively. Reaction with hydrogen sulfide produces barium sulfide. Precipitation of many insoluble, or less soluble barium salts, may result from double replacement reaction when a barium hydroxide aqueous solution is mixed with many solutions of other metal salts.[17]
Reactions of barium hydroxide with ammonium salts are strongly endothermic. The reaction of barium hydroxide octahydrate with ammonium chloride[18][19] or[20] ammonium thiocyanate[20][21] is often used as a classroom chemistry demonstration, producing temperatures cold enough to freeze water and enough water to dissolve the resulting mixture.
Safety
[edit]Barium hydroxide presents the same hazards such as skin irritation and burns as well as eye damage, just as the other strong bases and as other water-soluble barium compounds: it is corrosive and toxic. [citation needed]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Sortierte Liste: pKb-Werte, nach Ordnungszahl sortiert. - Das Periodensystem online" (in German).
- ^ Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ^ (1960). Gmelins Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie (8. Aufl.), Weinheim: Verlag Chemie, p. 289.
- ^ Kuske, P.; Engelen, B.; Henning, J.; Lutz, H.D.; Fuess, H.; Gregson, D. "Neutron diffraction study of Sr(OH)2(H2O) and beta-Ba(OH)2*(H2O)" Zeitschrift für Kristallographie (1979-2010) 1988, vol. 183, p319-p325.
- ^ Manohar, H.; Ramaseshan, S. "The crystal structure of barium hydroxide octahydrate Ba (OH)2(H2O)8" Zeitschrift für Kristallographie, Kristallgeometrie, Kristallphysik, Kristallchemie 1964. vol. 119, p357-p374
- ^ Robert Kresse, Ulrich Baudis, Paul Jäger, H. Hermann Riechers, Heinz Wagner, Jochen Winkler, Hans Uwe Wolf, "Barium and Barium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2007 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_325.pub2
- ^ Mendham, J.; Denney, R. C.; Barnes, J. D.; Thomas, M. J. K. (2000), Vogel's Quantitative Chemical Analysis (6th ed.), New York: Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-582-22628-7
- ^ Meyer, K.; Bloch, H. S. (1945). "Naphthoresorcinol". Org. Synth. 25: 73; Coll. Vol. 3: 637.
- ^ Brown, G. B. (1946). "Methylsuccinic acid". Org. Synth. 26: 54; Coll. Vol. 3: 615.
- ^ Ford, Jared H. (1947). "β-Alanine". Org. Synth. 27: 1; Coll. Vol. 3: 34.
- ^ Anslow, W. K.; King, H.; Orten, J. M.; Hill, R. M. (1925). "Glycine". Org. Synth. 4: 31; Coll. Vol. 1: 298.
- ^ Durham, L. J.; McLeod, D. J.; Cason, J. (1958). "Methyl hydrogen hendecanedioate". Org. Synth. 38:55; Coll. Vol. 4:635.
- ^ Chaudhari, M. R.; Kulkarni, Y. A.; Gokhale, S. B. (6 October 2008). Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology. Pragati Books Pvt. ISBN 9788185790169.
- ^ Thorpe, J. F.; Kon, G. A. R. (1925). "Cyclopentanone". Org. Synth. 5: 37; Coll. Vol. 1: 192.
- ^ Conant, J. B.; Tuttle, Niel. (1921). "Diacetone alcohol". Org. Synth. 1: 45; Coll. Vol. 1: 199.
- ^ Karabinos, J. V. (1956). "γ-lactone". Org. Synth. 36: 38; Coll. Vol. 4: 506.
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ "Endothermic Reactions of Hydrated Barium Hydroxide and Ammonium Chloride". UC San Diego. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- ^ Endothermic Solid-Solid Reactions
- ^ a b Camp, Eric. "Endothermic Reaction". Univertist of Washington. Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- ^ "Endothermic solid-solid reactions" (PDF). Classic Chemistry Demonstrations. The Royal Society of Chemistry. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2014.