West Prussia
| West Prussia Westpreußen (German) | |
|---|---|
| Province of Prussia | |
| 1773–1829 1878–1919 | |
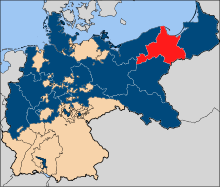 West Prussia (red), within the Kingdom of Prussia (blue), within the German Empire, as of 1878. | |
 West Prussia | |
| Anthem | |
| Westpreußenlied "Song of West Prussia" (1878–1919) | |
| Capital | Marienwerder (1773–1793, 1806–1813) Danzig (1793–1806, 1813–1920) |
| Demonym | West Prussian |
| Area | |
• 1910 | 25,534 km2 (9,859 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1910 | 1,703,474 |
| History | |
• Established | 1773 |
• Division by Napoleon | 1806 |
• Restored | 1815 |
| 1824–1878 | |
| 1919 | |
• Disestablished | 1919 |
| Political subdivisions | Danzig Marienwerder |
| Today part of | Poland |
The Province of West Prussia (German: Provinz Westpreußen; Kashubian: Zôpadné Prësë; Polish: Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1919. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth annexed in the First Partition of Poland. West Prussia was dissolved in 1829 and merged with East Prussia to form the Province of Prussia, but was re-established in 1878 when the merger was reversed and became part of the German Empire. From 1918, West Prussia was a province of the Free State of Prussia within Weimar Germany, losing most of its territory to the Second Polish Republic and the Free City of Danzig in the Treaty of Versailles. West Prussia was dissolved in 1920, and its remaining western territory was merged with Posen to form Posen-West Prussia, and its eastern territory merged with East Prussia as the Region of West Prussia district.
West Prussia's provincial capital alternated between Marienwerder (present-day Kwidzyn, Poland) and Danzig (Gdańsk, Poland) during its existence. West Prussia was notable for its ethnic and religious diversity due to immigration and cultural changes, with the population becoming mixed over the centuries. Since the early Middle Ages the bulk of the region was inhabited by West Slavic Lechitic tribes (Pomeranians in the Pomerelia region and Masovians in Kulmerland), while the actual Old Prussians (Pomesanians and Pogesanians) populated only the remaining part of the territory lying to the east of the Vistula River. The Teutonic Order's conquest of the region resulted in German colonization in the 14th century. As a result of Germanisation, Germans became in the middle of the 19th century the most numerous ethnic group in West Prussia as a whole, remaining as such until the dissolution of the province in 1920, though their distribution was uneven: their majority was concentrated in Danzig, the western lands of the province, along the Vistula river, and in the Pomesanian and Pogesanian portion of the province located east of the Vistula, with a small admixture of Poles (Gedanians and Powiślans). Meanwhile, Poles (Kociewians, Borowians and Chełminians) as well as Kashubians continued to predominate in parts of Pomerelian territories west of Vistula and in parts of the Chełmno Land, forming altogether around 36% of the population of the province as a whole. There were also sizeable minorities of Mennonites and Jews settling in the region.
Geography
[edit]
The landscape of West Prussia consisted of the lower reaches of the Vistula River (German: Weichsel, Polish: Wisła) near its mouth on the Baltic Sea, and neighboring lands to the west and east.
In the west, the province shared a border with easternmost Brandenburg, and comprised those lands between the provinces of Posen and Pomerania. This region of the province was characterized by the Baltic Uplands, with southward flowing rivers joining the Noteć (German: Netze). The Brda (German: Brahe) drains much of this area, joining the Vistula after passing through Bydgoszcz (German: Bromberg). Numerous large expanses of woodland, including the Tuchola Forest, were located in this part of the province. Further north near the sea is the Kashubian Lake District, where the highest point of the former province, Wieżyca (German: Turmberg), reaches 329 meters above sea level. The headwaters of Pomeranian rivers such as the Słupia (German: Stolpe) and Łeba (German: Leba) are located in these uplands.
In the north was the Baltic coast, consisting of a graded shoreline with landmarks such as the Hel Peninsula stretching 35 kilometers into the Gdańsk Bay, and the Vistula Fens where that river meets the sea. The Vistula delta encompasses a heavily cultivated area of approximately 2,000 square kilometers of land, much of it below sea level. The Nogat river, a distributary of the Vistula, flows to the northeast past the city of Malbork (German: Marienburg) and into the Vistula Lagoon. Further east near Elbląg (German: Elbing), the border with East Prussia crossed the Vistula Spit, Vistula Lagoon, and the Elbląg Upland.
In the southeast, the course of the Vistula river forms a wide, flat plain, with adjacent escarpments sometimes exceeding 60 meters in height above the river valley. This area includes the fertile Chełmno Land (German: Kulmerland), with historic cities such as Chełmno (German: Kulm), Toruń (German: Thorn), and Grudziądz (German: Graudenz). The Chełmno Land stretched eastward to the border with East Prussia, partially bound on the south by the path of the river Drwęca (German: Drewenz), which formed part of the province's southeastern border with Congress Poland and the Russian Empire.
History
[edit]Context
[edit]

The region of Pomerelia or Gdańsk Pomerania, historically Polish and never inhabited by Old Prussians, was forcibly occupied by the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights in 1308, following an invasion of Poland under the pretext of helping the King Władysław I Łokietek to quell a rebellion, with subsequent Teutonic atrocities against the Polish population, such as the Slaughter of Gdańsk. The possession of Danzig and Pomerelia by the Teutonic Order was questioned consistently by the Polish kings Władysław I and Casimir the Great in legal suits in the papal court in 1320 and 1333.[1] Both times, as well as in 1339, the Teutonic Knights were ordered by the Pope to return Pomerelia and other lands back to Poland, but did not comply.[1] These events resulted in a series of Polish–Teutonic Wars throughout the 14th and 15th centuries. Under the Teutonic rule, an influx of western, mainly German-speaking farmers, traders and craftsmen was encouraged. Subsequent rebellions organized by the local population against the Teutonic state, initially by the Lizard Union and later by the Prussian Confederation, both pledging allegiance to the Polish king, caused the Thirteen Years' War which ultimately led to the Second Peace of Thorn, when most of the region and was reclaimed by Poland and henceforth formed Royal Prussia, consisting of the originally Polish Pomerelia and Chełmno Land, expanded by the addition of parts of the formerly Old Prussian territories of Pomesania, Pogesania and Warmia. The region had initially a degree of autonomy with an own local legislature, the Prussian Estates, and maintaining its own laws, customs and rights, but was ultimately re-absorbed directly into the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, following the Union of Lublin in 1569. The locally spoken language differed among social classes, with the aristocracy and urban burghers initially highly Germanised as a result of earlier Teutonic policies, but gradually Polonized in the later years, while the peasantry continued as predominantly Kashubian- and Polish-speaking.[2] A small area in the west of Pomerelia, the Lauenburg and Bütow Land, was granted to the rulers of Pomerania as a Polish fief before it was reintegrated with Poland in 1637, and later again transformed into a Polish fief, which it remained until the First Partition of Poland.
East Prussia around Königsberg, on the other hand, remained with the State of the Teutonic Knights, who were reduced to vassals of the Polish kings. Their territory was secularised to become the Lutheran Duchy of Prussia according to the 1525 Treaty of Kraków and the Prussian Homage. The duchy was later ruled in personal union with the Imperial Margraviate of Brandenburg from 1618. The Hohenzollern rulers of Brandenburg-Prussia were able to remove the Polish suzerainty by the 1657 Treaty of Wehlau, taking advantage of the Russo-Swedish Deluge, shortly thereafter transforming their possessions into a kingdom. This development turned out to be fatal to the Polish monarchy, as the two parts of the rising Kingdom of Prussia were separated by Polish land. Subsequently, the newly established kingdom entered into an alliance with Austria and Russia, invading Polish territories.
Even though some German authors viewed the establishment of West Prussia as a historic reunification of the lands of the Teutonic State, officially, the Prussian government shunned from justifying the annexation by such argument. The reason was that the Teutonic Order still called for reestablishment of their rule over East- and West Prussia. [3]
Establishment
[edit]In the 1772 First Partition of Poland the Prussian king Frederick the Great took the occasion to annex most of Royal Prussia. The addition gave Prussia a land connection between the Province of Pomerania and East Prussia, cutting off the Polish access to the Baltic Sea and rendering East Prussia more readily defensible in the event of war with the Russian Empire. The annexed voivodeships of Pomerania (i.e. Pomerelia) excluding the City of Danzig, Malbork (German: Marienburg) and Chełmno (German: Kulm) excluding the City of Thorn (Polish: Toruń) were incorporated into the Province of West Prussia the following year, along with the formerly East Prussian Marienwerder Kreis. Ermland (Polish: Warmia) became part of East Prussia while the annexed parts of Greater Poland and Kuyavia formed a separate Netze District located to the south. The Partition Sejm ratified the cession on 30 September 1773, complemented by renouncement by the Polish king of his royal title in regard to Prussia. Thereafter, Frederick finally started to style himself "King of Prussia" rather than "King in Prussia." Both abovementioned exempted cities were ultimately captured by the Kingdom of Prussia upon the Second Partition of Poland in 1793.
The Polish administrative and legal code was replaced by the Prussian system, and 750 schools were built from 1772-1775.[4] Both Protestant and Roman Catholic teachers taught in West Prussia, and teachers and administrators were encouraged to be able to speak both German and Polish. Frederick II of Prussia also advised his successors to learn Polish, a policy followed by the Hohenzollern dynasty until Frederick III decided not to let William II learn Polish.[4] Despite this, Frederick II (Frederick the Great) looked askance upon many of his new citizens. In a letter from 1735, he calls them "dirty" and "vile apes".[5] He had nothing but contempt for the szlachta, the numerous Polish nobility, and wrote that Poland had "the worst government in Europe with the exception of Ottoman Empire".[6] He considered West Prussia less civilized than Colonial Canada[7] and compared the Poles to the Iroquois.[6] In a letter to his brother Henry, Frederick wrote about the province that "it is a very good and advantageous acquisition, both from a financial and a political point of view. In order to excite less jealousy I tell everyone that on my travels I have seen just sand, pine trees, heath land and Jews. Despite that there is a lot of work to be done; there is no order, and no planning and the towns are in a lamentable condition."[8] Frederick invited German immigrants to redevelop the province.[4][9] Many German officials also regarded the Poles with contempt.[7] According to the Polish historian Jerzy Surdykowski, Frederick the Great introduced 300,000 German colonists.[10] According to Christopher Clark, 54 percent of the annexed area and 75 percent of the urban population were German-speaking Protestants.[11] Further Polish areas were annexed in the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, now including the cities of Danzig (Gdańsk) and Thorn (Toruń).
Napoleonic Wars
[edit]After the defeat of Prussia by the Napoleonic French Empire at the 1806 Battle of Jena-Auerstedt followed by the Treaties of Tilsit, West Prussia lost its southern territory in the vicinity of Thorn and Kulm (Chełmno) to the short-lived Duchy of Warsaw; it also lost Danzig, which was a Free City from 1807 until 1814. After the final defeat of Napoleon in 1815, Danzig, Kulm, and Thorn were returned to West Prussia by resolution of the Vienna Congress. Some of the areas of Greater Poland annexed in 1772 that had formed the Netze District were added to West Prussia as well (the remainder became part of the Grand Duchy of Posen).
Restoration
[edit]
Legend for the districts:
The Congress of Vienna established the German Confederation (German: Deutscher Bund), an association of 39 German-speaking states in Central Europe under the nominal leadership of Austrian Empire, as a replacement for the dissolved Holy Roman Empire. Its boundaries largely followed those of its predecessor, the Holy Roman Empire, defining the territory of Germany for much of the 19th century.
Except for the Lauenburg and Bütow Land and the former Starostwo of Draheim, the Prussian lands which had been outside the Empire remained outside the Confederation, namely the former Ducal Prussia and those territories gained during the partitions of Poland. This included both predominantly Polish- or Kashubian-speaking areas (former Greater Poland and Pomerelia within West Prussia and the Grand Duchy of Posen) and German-speaking areas (Malbork Land within West Prussia and most of East Prussia). A failed attempt to include these lands in the German Empire (1848–49) was undertaken by the Frankfurt Parliament.
In 1815, the province was administratively subdivided into the Regierungsbezirke Danzig and Marienwerder. From 1829 to 1878, West Prussia was combined with East Prussia to form the Province of Prussia, after which they were re-established as separate provinces. In 1840, King Frederick William IV of Prussia sought to reconcile the state with the Catholic Church and the kingdom's Polish subjects by granting amnesty to imprisoned Polish bishops and by re-establishing Polish instruction in schools in districts having Polish majorities.
Incorporation into Germany
[edit]
With rise of nationalism, the Hohenzollern-ruled territory increasingly became a target of aggressive Germanisation efforts, German settlement, anti-Catholic campaigns (Kulturkampf), as well as disfranchisement and expropriations of Poles, and was finally annexed into Germany following the North German Confederation Treaty (1866). The Polish historian Andrzej Chwalba cites Germanization measures that included:
- Ethnic Germans were favoured in government contracts, and only they won them over Poles.[12]
- Ethnic Germans were also promoted in investment plans and supply contracts.[12]
- German craftsmen in Polish territories received the best locations in cities from authorities so that they could start their own business and prosper.[12]
- Soldiers received orders that banned them from buying in Polish shops and from Poles under the threat of arrest.[12]
- German merchantmen were encouraged to settle in Polish territories.[12]
- Tax incentives and beneficial financial arrangements were proposed to German officials and clerks if they would settle in Polish-inhabited provinces.[12]
At the time of German Unification in 1871, the Kingdom of Prussia was the largest and dominant part of the North German Confederation, the predecessor of the newly-formed German Empire.
In the German census of 1910, the population of West Prussia was put at 1,703,474, of whom around 64 percent listed their first language as German, 28 percent Polish and 7 percent Kashubian. According to Polish authors the real share of Poles and Kashubians was 43% (rather than 35.5% as in official figures), but many of them were counted as Catholic Germans by Prussian census clerks.[14]
Dissolution
[edit]In 1910, ethnic Poles were between 36% and 43% of West Prussia's populace.[14] After the Treaty of Versailles in 1919, most of pre-war West Prussia's territory (62%) and population (57%, the majority of whom were Polish) was granted to the Second Polish Republic or the Free City of Danzig (8% of territory, 19% of population), while parts in the west (18% of territory, 9% of population) and east (12% of territory, 15% of population) of the former province remained in Weimar Germany.[15] The western remainder formed Grenzmark Posen-West Prussia in 1922, while the eastern remainder became part of Regierungsbezirk West Prussia within East Prussia.
The 1920 East Prussian plebiscite was also held in the eastern part of West Prussia, which was known as the Marienwerder Plebiscite Area, and included partially or fully, the districts of Marienwerder, Stuhm, Rosenberg and Marienburg. The residents of this region voted by a majority of 92.4% to remain with Germany.[16]
| West Prussia | Area in 1910 in km2 | Share of territory | Population in 1910 | After WW1 part of: | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Given to: | 25,580 km2 [17] | 100% | 1,703,474 | Divided between: | |
| Poland | 15,900 km2 [17] | 62% [18] | 57% [18] | Pomeranian Voivodeship | [Note 1] |
| Free City Danzig | 1,966 km2 | 8% | 19% | Free City of Danzig | |
| Germany | 2,927 km2 | 11% | 15% | East Prussia | [Note 2] |
| 4,787 km2 | 19% | 9% | Posen-West Prussia[19] | [Note 3] |
World War II
[edit]In 1939, the region was invaded, then included in the Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia within Nazi Germany during World War II and settled with 130,000 German colonists,[20] while between 120,000 and 170,000 Poles and Jews were removed by the Germans through expulsion, massacres, enslavement or killed in extermination camps.[21] As in all other areas, Poles and Jews were classified as "Untermenschen" by the German state, with their fate being slavery and extermination, the latter in particular during Intelligenzaktion Pommern, as well as in the Stutthof concentration camp. Later in the war, many West Prussian Germans fled westward as the Red Army advanced on the Eastern Front. All of the areas occupied by Nazis were restored to Poland according to the post-war Potsdam Agreement in 1945, along with further neighbouring areas of former Nazi Germany and areas that had been part of Germany before. The vast majority of the remaining German population of the region that had not fled was subsequently expelled westward. Many German civilians were deported to labor camps like Vorkuta in the Soviet Union, where a large number of them perished or were later reported missing. In 1949, the refugees established the non-profit Landsmannschaft Westpreußen to represent West Prussians in the Federal Republic of Germany.
Historical population
[edit]

] Perhaps the earliest estimations on ethnic or national structure of West Prussia are from 1819. At that time West Prussia had 630,077 inhabitants, including 327,300 Poles (52%), 290,000 Germans (46%) and 12,700 Jews (2%).[22]

| Ethnic group | Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage | |
| Poles (Polen) | 327,300 | 52% |
| Germans (Deutsche) | 290,000 | 46% |
| Jews (Juden) | 12,700 | 2% |
| Total | 630,077 | 100% |
Karl Andree, "Polen: in geographischer, geschichtlicher und culturhistorischer Hinsicht" (Leipzig 1831), gives the total population of West Prussia as 700,000 – including 50% Poles (350,000), 47% Germans (330,000) and 3% Jews (20,000).[23]

The population more than doubled during the next seven decades, reaching 1,433,681 inhabitants (including 1,976 foreigners) in 1890.
- 1875 – 1,343,057
- 1880 – 1,405,898
- 1890 – 1,433,681 (717,532 Catholics, 681,195 Protestants, 21,750 Jews, others)
- 1900 – 1,563,658 (800,395 Catholics, 730,685 Protestants, 18,226 Jews, others)
- 1905 – 1,641,936
- 1910 – 1,703,474 (according to German statistics there were 35.5% Poles)[14]
According to the German census of 1910, in areas that became Polish after 1918, 42% of the populace were Germans (including German military, officials and colonists), while the Polish census of 1921 found 19% of Germans in the same territory.[24]
Contemporary sources in late 19th and early 20th centuries gave the number of Kashubians between 80,000–200,000.[25]
Subdivisions
[edit]Note: Prussian provinces were subdivided into districts called Kreise (singular Kreis, abbreviated Kr.). Cities would have their own Stadtkreis (urban district) and the surrounding rural area would be named for the city, but referred to as a Landkreis (rural district).
| District (Kreis) | Regierungsbezirk | Polish name | Population | German | % | Polish / Kashubian / Bilingual | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berent | Danzig | Powiat kościerski | 55,976 | 23,682 | 42.3% | 32,287 | 57.7% |
| Danziger Höhe | Danzig | Powiat Gdańskie Wyżyny | 53,506 | 47,397 | 88.6% | 6,071 | 11.3% |
| Danziger Niederung | Danzig | Powiat Gdańskie Niziny | 36,345 | 36,008 | 99.1% | 327 | 0.9% |
| Stadtkreis Danzig | Danzig | Powiat grodzki Gdańsk | 170,337 | 164,343 | 96.5% | 5,521 | 3.2% |
| Dirschau | Danzig | Powiat tczewski | 42,723 | 27,865 | 65.2% | 14,846 | 34.7% |
| Landkreis Elbing | Danzig | Powiat elbląski | 38,611 | 38,558 | 99.9% | 48 | 0.1% |
| Stadtkreis Elbing | Danzig | Powiat grodzki Elbląg | 58,636 | 58,330 | 99.5% | 248 | 0.4% |
| Karthaus | Danzig | Powiat kartuski | 69,891 | 19,319 | 27.6% | 50,568 | 72.4% |
| Marienburg | Danzig | Powiat malborski | 62,999 | 61,050 | 96.9% | 1,924 | 3.1% |
| Neustadt | Danzig | Powiat wejherowski | 61,620 | 30,932 | 50.2% | 30,661 | 49.8% |
| Preußisch Stargard | Danzig | Powiat starogardzki | 65,427 | 17,165 | 26.2% | 48,250 | 73.7% |
| Putzig | Danzig | Powiat pucki | 26,548 | 7,970 | 30.0% | 18,561 | 69.9% |
| Total (Danzig) | Danzig | Rejencja gdańska łącznie | 742,619 | 532,619 | 71.7% | 209,312 | 28.2% |
| Briesen | Marienwerder | Powiat wąbrzeski | 49,506 | 24,007 | 48.5% | 25,487 | 51.5% |
| Culm | Marienwerder | Powiat chełmiński | 50,069 | 23,345 | 46.6% | 26,709 | 53.3% |
| Deutsch Krone | Marienwerder | Powiat wałecki | 62,182 | 61,143 | 98.3% | 1,022 | 1.6% |
| Flatow | Marienwerder | Powiat złotowski | 69,186 | 50,648 | 73.2% | 18,531 | 26.8% |
| Landkreis Graudenz | Marienwerder | Powiat grudziądzki | 48,818 | 28,755 | 58.9% | 20,046 | 41.1% |
| Stadtkreis Graudenz | Marienwerder | Powiat grodzki Grudziądz | 40,325 | 34,193 | 84.8% | 6,076 | 15.1% |
| Konitz | Marienwerder | Powiat chojnicki | 63,723 | 28,032 | 44.0% | 35,670 | 56.0% |
| Löbau | Marienwerder | Powiat lubawski | 59,037 | 12,119 | 20.5% | 46,911 | 79.5% |
| Marienwerder | Marienwerder | Powiat kwidzyński | 68,426 | 42,465 | 62.1% | 25,944 | 37.9% |
| Rosenberg | Marienwerder | Powiat suski | 54,550 | 50,194 | 92.0% | 4,321 | 7.9% |
| Schlochau | Marienwerder | Powiat człuchowski | 67,157 | 56,648 | 84.4% | 10,488 | 15.6% |
| Schwetz | Marienwerder | Powiat świecki | 89,712 | 42,233 | 47.1% | 47,465 | 52.9% |
| Strasburg | Marienwerder | Powiat brodnicki | 62,142 | 21,097 | 33.9% | 41,026 | 66.0% |
| Stuhm | Marienwerder | Powiat sztumski | 36,527 | 20,923 | 57.3% | 15,583 | 42.7% |
| Landkreis Thorn | Marienwerder | Powiat toruński | 59,317 | 27,751 | 46.8% | 31,493 | 53.1% |
| Stadtkreis Thorn | Marienwerder | Powiat grodzki Toruń | 46,227 | 30,505 | 66.0% | 15,576 | 33.7% |
| Tuchel | Marienwerder | Powiat tucholski | 33,951 | 11,265 | 33.2% | 22,656 | 66.7% |
| Total (Marienwerder) | Marienwerder | Rejencja kwidzyńska łącznie | 960,855 | 565,323 | 58.8% | 395,004 | 41.1% |
| Total (West Prussia) | - | - | 1,703,474 | 1,097,942 | 64.5% | 604,316 | 35.5% |
Office holders
[edit]- Administration of West Prussia before 1919
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Matthew Kuefler, The Boswell Thesis: Essays on Christianity, Social Tolerance, and Homosexuality, [1]
- ^ Dr Jaroslav Miller. Urban Societies in East-Central Europe, 1500–1700. Ashgate Publishing. p. 179.
- ^ Gerard Labuda. "Die Revision der Geschichte Preußens - Errungenschaften und Forschungspläne". Preussen Deutschland Polen im Urteil polnsicher Historiker Band 1. Einzelveröffentlichungen der Historischen Kommission zu Berlin. Vol. 37. p. 159.
- ^ a b c Koch, p. 136
- ^ Przegląd humanistyczny, Tom 22, Wydania 3–6 Jan Zygmunt Jakubowski Państwowe Wydawn. Naukowe, 2000, page 105
- ^ a b Ritter, p. 192
- ^ a b David Blackbourn. "Conquests from Barbarism": Interpreting Land Reclamation in 18th Century Prussia. Harvard University. Accessed 24 May 2006.
- ^ MacDonogh, p. 363
- ^ Norbert Finszch and Dietmar Schirmer. Identity and Intolerance: Nationalism, Racism, and Xenophobia in Germany and the United States. Cambridge University Press, 2006. ISBN 0-521-59158-9
- ^ Duch Rzeczypospolitej Jerzy Surdykowski - 2001 Wydawn. Nauk. PWN, 2001, page 153
- ^ Christopher M. Clark (2006). Iron Kingdom: the rise and downfall of Prussia, 1600-1947. Harvard University Press. p. 233. ISBN 978-0-674-02385-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g Andrzej Chwalba, Historia Polski 1795-1918, pp. 461-463
- ^ Bideleux, Robert; Jeffries, Ian (1998), A history of eastern Europe: crisis and change (1st ed.), Routledge, p. 180,
It systematically Germanicized "eastern" place names and public signs, fostered German cultural imperialism, and provided financial and other inducements for German farmers, officials, clergy, and teachers to settle and work in the east. After Bismarck's fall in 1890, Kaiser Wilhelm II actively encouraged all this. Not only did he provide large benefactions...
- ^ a b c Kozicki, Stanislas (1918). The Poles under Prussian rule. London: Polish Press Bur. p. 5.
- ^ Nadobnik, Marcin (1921). "Obszar i ludność b. dzielnicy pruskiej [Area and population of the former Prussian territory]" (PDF). AMUR - Adam Mickiewicz University Repository (in Polish).
- ^ "Plebiszite" (PDF). 2007-06-09. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2007-06-09. Retrieved 2021-05-07.
- ^ a b Weinfeld, Ignacy (1925). Tablice statystyczne Polski: wydanie za rok 1924 [Poland's statistical tables: edition for year 1924]. Warsaw: Instytut Wydawniczy "Bibljoteka Polska". p. 2.
- ^ a b Nadobnik, Marcin (1921). "Obszar i ludność b. dzielnicy pruskiej [Area and population of former Prussian district]" (PDF). Ruch Prawniczy, Ekonomiczny i Socjologiczny. 1 (3). Poznań – via AMUR - Adam Mickiewicz University Repository.
- ^ "Die Grenzmark Posen-Westpreußen Übersichtskarte". Gonschior.de.
- ^ Bogdan Chrzanowski: Wypędzenia z Pomorza. Biuletyn IPN nr 5/2004, May 2004.
- ^ WYSIEDLENIA Z ZIEM ZACHODNICH RZECZYPOSPOLITEJ W OKRESIE OKUPACJI NIEMIECKIEJ doctor Andrzej Gąsiorowski Stutthof Museum
- ^ a b Hassel, Georg (1823). Statistischer Umriß der sämmtlichen europäischen und der vornehmsten außereuropäischen Staaten, in Hinsicht ihrer Entwickelung, Größe, Volksmenge, Finanz- und Militärverfassung, tabellarisch dargestellt; Erster Heft: Welcher die beiden großen Mächte Österreich und Preußen und den Deutschen Staatenbund darstellt. Verlag des Geographischen Instituts Weimar. p. 42.
- ^ Andree, Karl (1831). Polen: in geographischer, geschichtlicher und culturhistorischer Hinsicht. Verlag von Ludwig Schumann. p. 212.
- ^ "This site can't be reached". web.ku.edu. Retrieved January 27, 2024.
- ^ "Kilka słów o Kaszubach i ich mowie: II. Obecne terytoryum etnograficzne szczepu pomorskiego | Kaszubska Strona Informacyjna". Retrieved 2024-01-27.
- ^ Belzyt, Leszek (1998). Sprachliche Minderheiten im preussischen Staat: 1815 - 1914 ; die preußische Sprachenstatistik in Bearbeitung und Kommentar. Marburg: Herder-Inst. ISBN 978-3-87969-267-5.
Notes
[edit]- ^ Poland received several cities and counties of West Prussia located east of the Vistula: Lubawa, Brodnica, Wąbrzeźno, Toruń, Chełmno, Grudziądz; as well as most of cities and counties of West Prussia located west of it: Świecie, Tuchola, Starogard Gdański, Kwidzyn (only part west of the Vistula), most of county Tczew, eastern part of county Złotów, part of county Człuchów, as well as counties Chojnice, Kościerzyna, Kartuzy, coastal Wejherowo and Puck with Gdynia; as well as a small western part of Danziger Höhe and areas around Janowo east of the Vistula.
- ^ Parts of West Prussia east of the Nogat and the Vistula Rivers, which remained in Germany after 1918, including the city and county of Elbląg and counties Malbork (part east of Nogat), Sztum, Kwidzyn (only the part east of the Vistula) and Susz, were incorporated to East Prussia as the Regency of West Prussia. The area of historical Pomesania had significant Polish minority.
- ^ Western part of West Prussia with county Wałcz and parts of counties Złotów and Człuchów (the latter two split between Poland and Germany). This area included 12 towns and cities: Człuchów, Debrzno, Biały Bór, Czarne, Lędyczek, Złotów, Krajenka, Wałcz, Mirosławiec, Człopa, Tuczno and Jastrowie. The area was home to significant Polish minority.
External links
[edit]- Blanke, Richard (1993). Orphans of Versailles. The University Press of Kentucky. p. 316. ISBN 0-8131-1803-4.
- Koch, H. W. (1978). A History of Prussia. New York: Barnes & Noble Books. p. 326. ISBN 0-88029-158-3.
- MacDonogh, Giles (2001). Frederick the Great: A Life in Deed and Letters. New York: St. Martin's Griffin. p. 436. ISBN 0-312-27266-9.
- Ritter, Gerhard (1974). Frederick the Great: A Historical Profile. Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 207. ISBN 0-520-02775-2.
- de Zayas, Alfred-Maurice (1994). A Terrible Revenge: The Ethnic Cleansing of the Eastern European Germans 1944–1950. New York: St. Martin's Press.
- Rota, Andrea (2010). Wiedersehen mit der Familie, Wiedersehen in der Heimat. SÖHNE von Volker Koepp. In Elena Agazzi, Erhard Schütz (Ed.): Heimkehr: Eine zentrale Kategorie der Nachkriegszeit. Geschichte, Literatur und Medien. Berlin: Duncker & Humblot. p. 257–268. ISBN 978-3-428-53379-4
External links
[edit]- www.westpreussen-online.de (in German)
- Administrative subdivision of the province in 1910 (in German)
- Das Westpreußenlied (Real Audio)
- West Prussia FAQ
- Extensive West Prussian Historical Materials Archived 2014-09-14 at the Wayback Machine
- East and West Prussia Gazetteer Archived 2007-01-05 at the Wayback Machine
- West & East Prussia Map Collection Archived 2013-09-09 at the Wayback Machine


